With digital inclusivity consistently gaining popularity, accessibility has become a major requirement as more and more lives are conducted online.
The internet is built to work for everyone, regardless of their device, language, location, or aptitude. But, to fully achieve that goal, and to make it usable for everyone with a connection, it must be able to account for users whose ability to engage with the world is challenged by a wide range of hearing, movement, vision, and cognitive disabilities.
Accessibility refers to a user’s capacity to access products/services with as reduced hindrance as possible commensurate with their individual condition. It’s a common misconception that accessibility is relegated only to people with disabilities. Aaron Sines from Big Drop says:
One of the most important factors influencing how consumers make purchase decisions today is corporate social responsibility (CSR). As companies seek to develop effective CSR strategies, web accessibility is one of the primary aspects of corporate sustainability reporting.
In many places, web accessibility is protected under various laws. In the U.S., the Workforce Rehabilitation Act of 1973 requires that all “electronic and information technology developed, procured, maintained, or used by the federal government be accessible to people with disabilities.”
Businesses that overlook accessibility are already being pressured to adapt their platforms for impaired users, and in some cases are losing e-customers and clients if no action is taken. As a result, denying accessibility, and failing to acknowledge it as a human right, has negative, reputational consequences. With this in mind, the sooner a business recognizes accessibility as a core value when developing a website or app, the better they will be known as a company that does not overlook consumers with disabilities, broadening the scope of their target audience and setting themselves up for a higher rate of conversion.
Because websites oftentimes do not incorporate requirements for people with disabilities, there are obstacles that make the internet completely inaccessible to them. Many parts of the internet are still not treated as public spaces are, so access is not guaranteed to everyone, regardless of ability. Big Drop’s Senior Director, James Weiss, stated:
Despite large, global efforts to simplify our lives through innovation, it’s still an unfortunate reality that the world isn’t yet able to fully support individuals challenged by an impairment. For too long, the digital accessibility gap widened for the disabled, just as it did for entities to offer access, but we can confidently say that the divide has been reduced considerably and we are collectively well on our way to blurring the lines between “abled” and “disabled”. Make no mistake, we still have a ways to go, but reaching this goal is now probable, not just possible.”
When creating a web presence for one of our clients, Northwell Health, our team at Big Drop made sure the site would follow all accessibility guidelines; ensuring digital inclusivity and an easily accessible experience for all. Here’s a look into how:
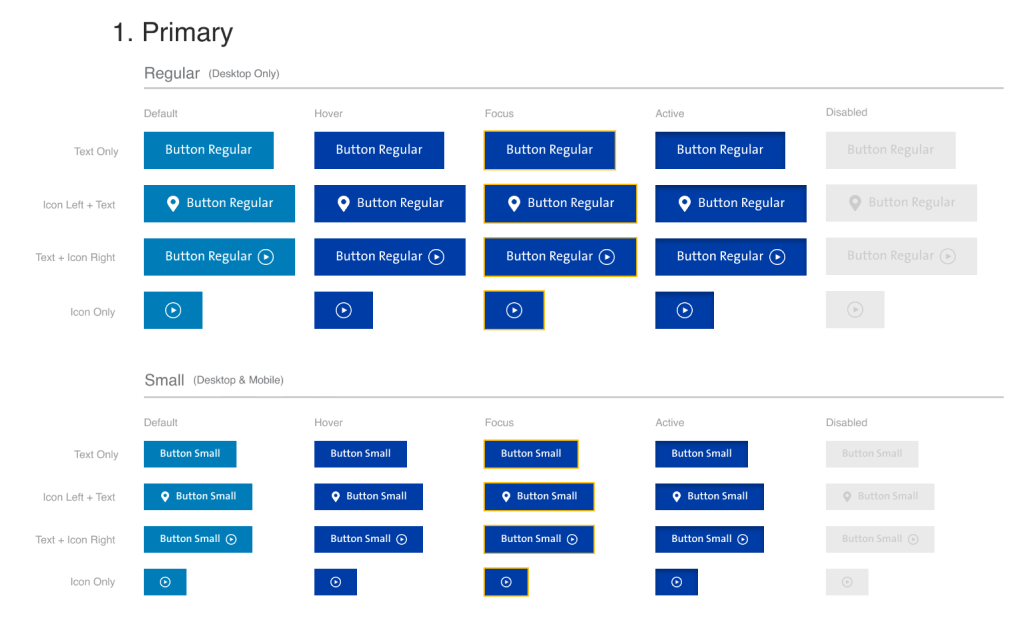
Image 1- Disabled users who rely on a keyboard to navigate, have trouble doing so without clear, visible focus states. A focus state shows users what is clickable, and it helps to identify what an element is. Focus’s job is to indicate what element the user is dealing with. The image above shows a piece of the style guide that reflects individual styles for the focus state of the site elements.
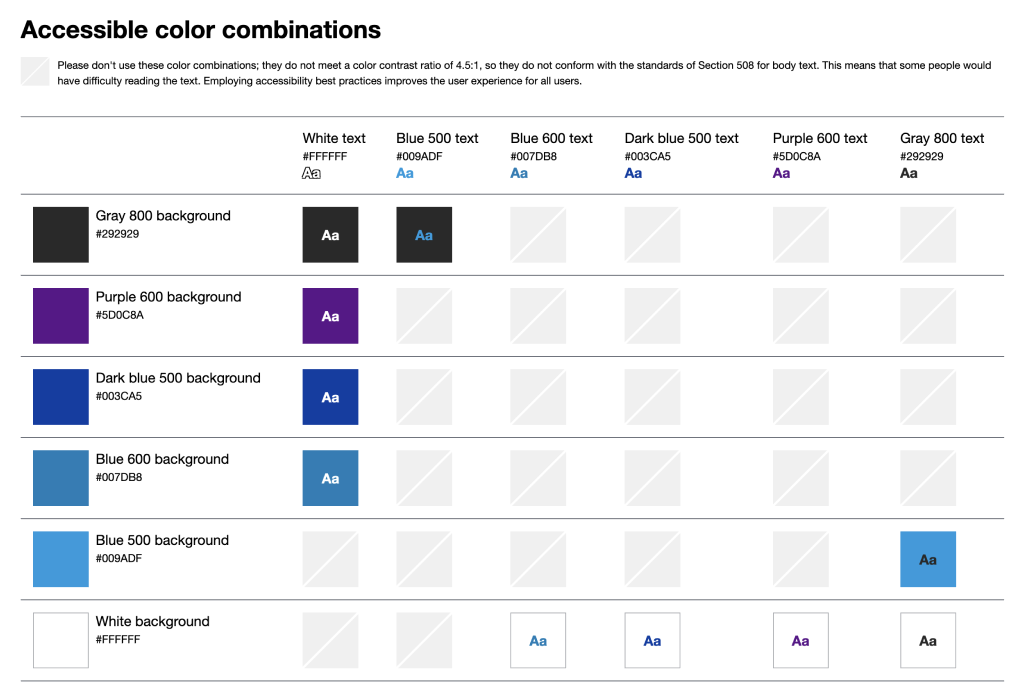
Image 2- People with visual impairments interpret color and contrast differently. Making colors accessible means combining colors with enough contrast so that the content is clearly distinguishable from the surrounding page. The accessible color matrix helps designers build color palettes with combinations that meet accessibility standards. The image above shows an example of an ADA-compliant color matrix.
Benefits
Web accessibility is not only ethical, and for that reason, sound business practice and legal obligation. It’s important to show and represent options for people with disabilities for no other reason than empathy sits at the cornerstone of good design. Companies that offer options for a variety of skill sets and disabilities can perceive, understand, navigate, engage with, and contribute meaningfully to their many presences when it is designed for any type of user.
Additionally, here are two main benefits associated with pursuing full Accessibility:
Increases In User Bases are realized by maximizing ease of use for all ability levels. This creates experiences for everyone to use and enjoy, no matter the context. Universal Design helps broaden the user pool at large, and because people with disabilities make up one of the largest demographics globally gains within customer bases can be seen from what would have been an untapped market.
Innovation is driven through accessibility. Google and Apple consider accessibility to be a core human right, and they strive to make their products better, more human-friendly. Microsoft’s Seeing AI project focuses on noticing images rather than just seeing them, in order to better communicate with blind people. Google’s Project Tango, for example, uses computer vision to help blind people be accurately placed in three-dimensional space. Google has also made advancements in the field of non-language processing, which is a method of processing noises and intonations for the benefit of the hearing-impaired. Kirill Yarovenko, Big Drop’s UX/UI lead, says:
We are living in a rapidly changing world and we need to work hard to keep up. Making your website accessible from the beginning will help your business attract more visitors and boost sales. So, people with disabilities can enjoy using a fully accessible site just as much as everyone else. Accessibility also contributes to SEO, which will allow your website to rank higher in search results and gain more organic visitors.”
Final Thoughts
We’ve reached a point where inclusion and accessible design can no longer be treated as an afterthought when it comes to effective design and experiences. How we make our products today or supply our services, as well as who we cater to and choose to include, will determine how long companies may survive and how they will be respected. Making the internet accessible benefits individuals and businesses.
International web standards define what is needed for accessibility. Check your rate of compliance here.
While creating digital presences, Big Drop can help ensure your site is ADA compliant. Get in touch.